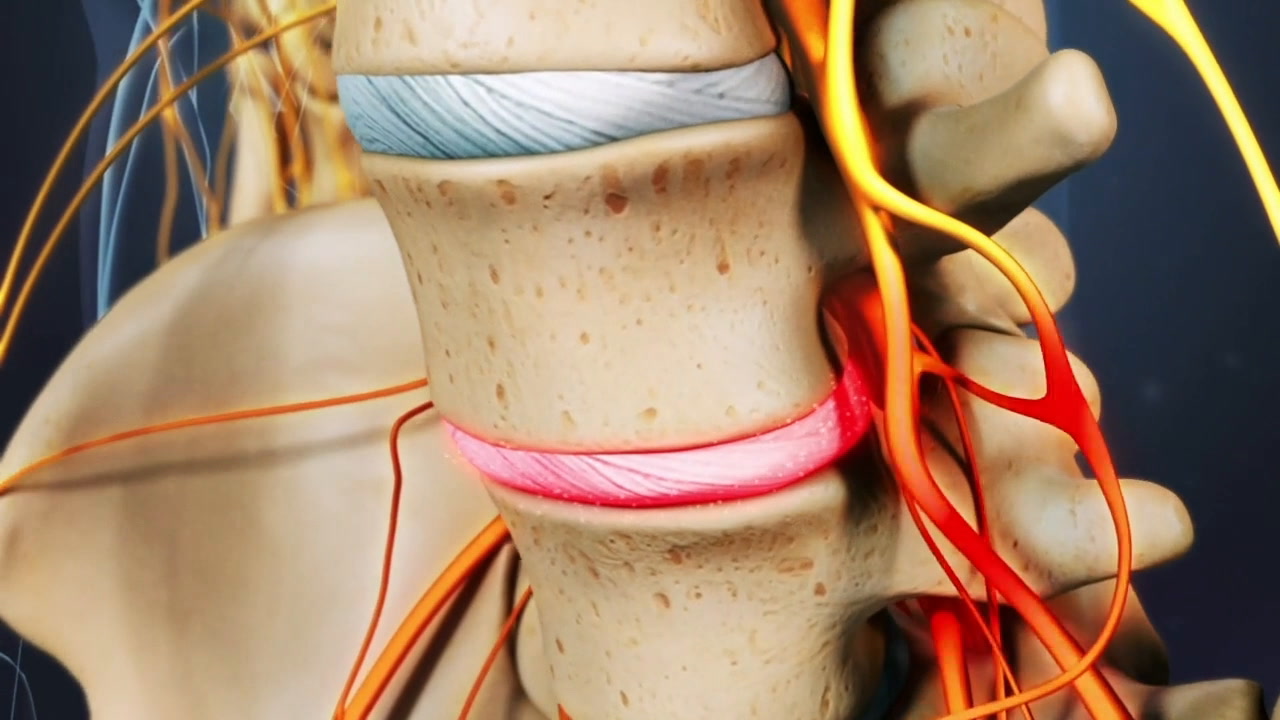
A herniated disc in the lower back can cause a range of symptoms varying from moderate pain in the lower back and buttock to widespread pain, numbness, and weakness in the leg and foot. The onset of symptoms is usually sudden with no apparent cause but is sometimes triggered by movements or activities that place stress on the disc, such as lifting or twisting.1Al Qaraghli MI, De Jesus O. Lumbar Disc Herniation. [Updated 2023 Aug 14]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK560878/
The severity of symptoms depends on how much the surrounding structures, such as the spinal nerve roots and the ligament behind the vertebrae and discs (posterior longitudinal ligament), are affected.
For most individuals, the symptoms and signs related to nerve roots are more prevalent and bothersome.
In This Article:
What a Lumbar Herniated Disc Feels Like
The symptoms of lumbar disc herniation most commonly affect the lower back, buttock, and parts of the thigh, leg, and/or foot on one side of the body.
Most individuals experience some combination of the following signs and symptoms:
Sharp, burning pain in the leg
Sciatica pain is usually the first symptom of a herniated disc in the low back.
A searing, burning pain that travels from the lower back through the buttock and into the thigh, leg, and/or foot is typically the first symptom of a herniated disc. For some individuals the pain is continuous, and for others, it comes and goes at different times during the day.1Al Qaraghli MI, De Jesus O. Lumbar Disc Herniation. [Updated 2023 Aug 14]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK560878/,2Alexander CE, Varacallo M. Lumbosacral Radiculopathy. [Updated 2023 Aug 4]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430837/ This type of pain occurs due to nerve root irritation between spinal levels L1 to S3.
In most cases, a nerve root between L4 to S3 is affected, and the pain travels along the path of the long sciatic nerve in the leg, which is why the term “sciatica” is commonly used to describe these symptoms. The medical term for sciatica is radicular pain.
Sciatica symptoms are also sometimes described as a1Al Qaraghli MI, De Jesus O. Lumbar Disc Herniation. [Updated 2023 Aug 14]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK560878/,2Alexander CE, Varacallo M. Lumbosacral Radiculopathy. [Updated 2023 Aug 4]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430837/:
- Stabbing sensation, similar to an intense jab
- Jolting sensation, similar to an electric shock
In sciatica, leg pain is usually more severe than back pain.
Read more about Sciatica Symptoms
Numbness, tingling, and weakness
Neurologic signs may also develop in the leg and foot, such as numbness, a tingling “pins and needles” sensation, and weakness.1Al Qaraghli MI, De Jesus O. Lumbar Disc Herniation. [Updated 2023 Aug 14]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK560878/,3Dydyk AM, Ngnitewe Massa R, Mesfin FB. Disc Herniation. [Updated 2023 Jan 16]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441822/ These symptoms are collectively referred to as radiculopathy, and their development indicates a worsening of a lumbar herniated disc.3Dydyk AM, Ngnitewe Massa R, Mesfin FB. Disc Herniation. [Updated 2023 Jan 16]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441822/
Radiculopathy affects specific areas of the thigh, leg, and foot depending on which nerve root is affected and on which side of the spine. In severe cases, these symptoms may lead to walking problems.
Sometimes, doctors use the term “lumbar radiculopathy” interchangeably with sciatica. Sciatica and lumbar radiculopathy can occur together, but technically, they are distinct medical problems.
Localized low back pain
Herniations pressing the posterior longitudinal ligament cause pain in the lower back area (axial pain), which ranges from a dull ache to a sharp pain and worsens with certain positions, such as sitting for long periods.1Al Qaraghli MI, De Jesus O. Lumbar Disc Herniation. [Updated 2023 Aug 14]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK560878/
Inability to lift the foot
Disc herniations that compress the L5 nerve root may cause weakness in the foot and big toe muscles – a condition known as foot drop – making it difficult to lift the front part of the foot off the ground.4Nori SL, Stretanski MF. Foot Drop. [Updated 2022 Jun 25]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554393/
Foot drop is characterized by an abnormal gait where the toes drag on the ground, or a person may lift their knee higher than usual to clear their foot while walking (steppage gait).4Nori SL, Stretanski MF. Foot Drop. [Updated 2022 Jun 25]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554393/
Muscle spasms and tension
Inflammation caused by a herniated disc can lead to muscle spasms in the low back.
Tightness, tenderness, and/or painful spasms occur in the lower back muscles as the body attempts to protect the injured nerve root.5Hirayama J, Yamagata M, Ogata S, Shimizu K, Ikeda Y, Takahashi K. Relationship between low-back pain, muscle spasm and pressure pain thresholds in patients with lumbar disc herniation. Eur Spine J. 2006;15(1):41-47. doi:10.1007/s00586-004-0813-2
Urge to continually move the legs
Restless leg syndrome (RLS) is characterized by an urge to continually move the legs accompanied by a sensation of crawling or pulling of the skin of the leg when at rest. This syndrome is a rare symptom of a herniated disc in the lower back.6Kocabicak E, Terzi M, Akpinar K, Paksoy K, Cebeci I, Iyigun O. Restless leg syndrome and sleep quality in lumbar radiculopathy patients. Behav Neurol. 2014;2014:245358. doi:10.1155/2014/245358
The exact reason why RLS develops is unknown, but research suggests that it is related to the increased levels of inflammatory proteins triggered by disc herniation.5Hirayama J, Yamagata M, Ogata S, Shimizu K, Ikeda Y, Takahashi K. Relationship between low-back pain, muscle spasm and pressure pain thresholds in patients with lumbar disc herniation. Eur Spine J. 2006;15(1):41-47. doi:10.1007/s00586-004-0813-2
What Makes Lumbar Herniated Disc Pain Worse or Better
Certain activities or positions that increase pressure on the herniated disc cause further inflammation or compression of the affected nerve root, exacerbating pain. These activities typically include, but are not limited to1Al Qaraghli MI, De Jesus O. Lumbar Disc Herniation. [Updated 2023 Aug 14]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK560878/,3Dydyk AM, Ngnitewe Massa R, Mesfin FB. Disc Herniation. [Updated 2023 Jan 16]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441822/:
- Bending forward at the waist
- Twisting the spine
- Coughing
- Sneezing
- Lifting heavy objects
- Prolonged sitting
Similarly, certain positions and activities reduce pressure on the disc and alleviate herniated disc symptoms.
These activities include:
- Lying on the side with a pillow between the knees
- Lying on the back with a pillow placed underneath the knees
- Sitting in a reclined position, such as on a reclining chair
- Lying flat on the back with the hips and knees bent at 90 degrees
For some individuals, engaging in short walks or staying active reduces the likelihood of pain recurrence or flare-ups.
Location of a Herniated Disc and Spinal Nerve Determine Where Symptoms Occur
Each nerve root in the low back is responsible for a distinct set of symptoms.
A disc usually herniates toward the back and to the side – where the nerve root lies. For this reason, the majority of herniations pose a risk of impacting the nerve root at that specific spinal level.
For example, a herniation at the L5-S1 spinal segment most likely affects the L5 nerve root, which exits the spinal canal at the L5-S1 segment.1Al Qaraghli MI, De Jesus O. Lumbar Disc Herniation. [Updated 2023 Aug 14]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK560878/ However, less commonly, the L5 nerve root can also be affected by disc herniations at L2-L3, L3-L4, or L4-L5.7Dydyk AM, Khan MZ, Singh P. Radicular Back Pain. [Updated 2022 Oct 24]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK546593/
Specific symptoms of a lumbar disc herniation based on the spinal segment affected are listed below1Al Qaraghli MI, De Jesus O. Lumbar Disc Herniation. [Updated 2023 Aug 14]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK560878/,7Dydyk AM, Khan MZ, Singh P. Radicular Back Pain. [Updated 2022 Oct 24]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK546593/:
- L1-L2 disc affecting the L1 spinal nerve root:
- Pain and sensory loss in the groin (inguinal region)
- Weakness in the hip muscles occurs in rare cases
- L2-L3 and L3-L4 discs affecting the L2 and L3 spinal nerve roots:
- Pain in the lower back, front of the thigh, knee, and/or long the inner side of the leg and foot
- Pain is worsened by sneezing, coughing, or straightening the leg
- L4-L5 disc affecting the L4 spinal nerve root:
- Pain lower back, front of the thigh, and the inner side of the leg.
- Weakness in the hip and knee muscles causing difficulty with lifting the leg, crossing the legs, or straightening the leg
- L5-S1 disc affecting the L5 nerve root:
- Pain in the lower back, buttocks, outer sides of the thigh and calf, top of the foot, and the big toe
- Numbness in the calf, top of the foot, and the web space between the first and second toe
- Weakness in the hip, knee, foot, and big toe muscles causing difficulty with bending and straightening the leg or moving the foot in different directions
- Inability to lift the foot off the ground (foot drop)
- S1-S2 disc affecting the S1 spinal nerve root:
- Pain in the buttock radiating to the back and side of the thigh and calf, bottom of the foot
- Numbness in the calf and along the side or bottom of the foot
- Weakness in the hip, knee, and foot muscles causing difficulty or an inability to walk on the toes
- Bowel and bladder dysfunction and/or sexual dysfunction occur in serious cases
It is also possible for more than one nerve root to be affected and cause overlapping symptoms. The symptoms may also be affected by normal variations in the patient’s lumbar spine anatomy, his or her perception of pain, and other factors.
In rare cases, compression of the spinal cord (myelopathy) may occur with a herniated disc at L1-L2 or in patients with a low-lying spinal cord, or compression of the cauda equina (cauda equina syndrome) may occur with a herniated disc between the L2-S1 spinal levels. These conditions are a medical emergency requiring urgent treatment.
Conditions That Mimic Lumbar Herniated Disc Symptoms
Some conditions mimic the symptoms and signs of a lumbar herniated disc, including8Kim K, Isu T, Morimoto D, et al. Common diseases mimicking lumbar disc herniation and their treatment. Mini-invasive Surgery. 2017;1(2). doi: 10.20517/2574-1225.2017.05:
- Piriformis syndrome: a condition where the piriformis muscle located deep in the buttock becomes inflamed and spasms, irritating the sciatic nerve. The symptoms may include buttock pain, and/or nerve pain that travels along the sciatic nerve down the thigh and leg.
- Sacroiliac (SI) joint dysfunction: a condition where the SI joint – situated on both sides of the sacrum at the base of the spine – moves too much or too little, causing pain in the buttock, lower back, and leg.
- Tarsal tunnel syndrome: dysfunction of the tibial nerve in the inner ankle. This condition causes sharp, shooting pain in the ankle area and along the sole of the foot.
The successful treatment of these conditions and/or a herniated disc depends on a thorough, accurate diagnosis. It is advisable to seek comprehensive medical evaluations to determine the precise cause of symptoms.
- 1 Al Qaraghli MI, De Jesus O. Lumbar Disc Herniation. [Updated 2023 Aug 14]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK560878/
- 2 Alexander CE, Varacallo M. Lumbosacral Radiculopathy. [Updated 2023 Aug 4]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430837/
- 3 Dydyk AM, Ngnitewe Massa R, Mesfin FB. Disc Herniation. [Updated 2023 Jan 16]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441822/
- 4 Nori SL, Stretanski MF. Foot Drop. [Updated 2022 Jun 25]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554393/
- 5 Hirayama J, Yamagata M, Ogata S, Shimizu K, Ikeda Y, Takahashi K. Relationship between low-back pain, muscle spasm and pressure pain thresholds in patients with lumbar disc herniation. Eur Spine J. 2006;15(1):41-47. doi:10.1007/s00586-004-0813-2
- 6 Kocabicak E, Terzi M, Akpinar K, Paksoy K, Cebeci I, Iyigun O. Restless leg syndrome and sleep quality in lumbar radiculopathy patients. Behav Neurol. 2014;2014:245358. doi:10.1155/2014/245358
- 7 Dydyk AM, Khan MZ, Singh P. Radicular Back Pain. [Updated 2022 Oct 24]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK546593/
- 8 Kim K, Isu T, Morimoto D, et al. Common diseases mimicking lumbar disc herniation and their treatment. Mini-invasive Surgery. 2017;1(2). doi: 10.20517/2574-1225.2017.05